这一次总结并发的一些初步知识,主要有select在实现并发服务器时的两点限制以及poll函数的使用,该函数也是一种I/O复用函数,与select基本相同。
1.select限制
用select实现的并发服务器,能达到的并发数,受两方面限制:
- 一个进程能打开的最大文件描述符限制。这可以通过调整内核参数。
- select中的fd_set集合容量的限制(FD_SETSIZE),这需要重新编译内核。
(1)可以通过以下命令查看一个进程能打开的最大文件描述符数:
ulimit -n
(2)以下命令可以进行调整:
ulimit -n 2048
系统所能打开的最大文件描述符个数也是有限的,跟内存大小有关。
2.poll函数
该函数没有FD_SETSIZE的限制。
- 头文件:#include <poll.h>
- 原型:int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
- 参数:
fds,通常是一个数组,将要关心的I/O描述符放入该数组中
nfds,加入数组中的个数,即,要检测的I/O个数
timeout,超时时间
(1)pollfd结构体:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
struct pollfd { int fd; //file descriptor to check, or <0 to ignore short events; //events of interest on fd short revents; //returned events }; |
其中events即感兴趣的事件,revents即返回的事件。如下罗列出events的取值: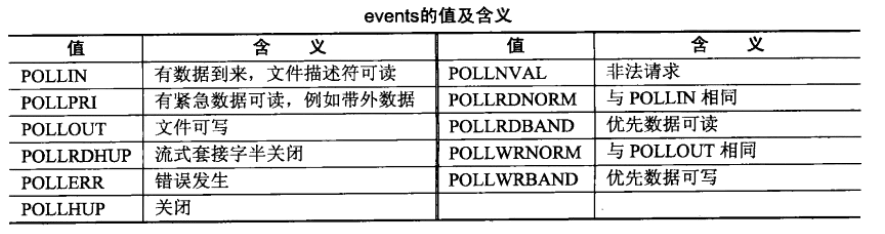
(2)poll 跟 select 还是很相似的,比较重要的区别在于poll 所能并发的个数跟FD_SETSIZE无关,只跟一个进程所能打开的文件描述符个数有关,可以在select 程序的基础上修改成poll 程序,在运行服务器端程序之前,使用ulimit -n 2048 将限制改成2048个,注意在运行客户端进程的终端也需更改,因为客户端也会有所限制,这只是临时性的更改,因为子进程会继承这个环境参数,而我们是在bash命令行启动程序的,故在进程运行期间,文件描述符的限制为2048个。
3.使用poll实现回射客户服务器程序
(1)echosrv.c
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 |
#include<stdio.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/socket.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #include<arpa/inet.h> #include<netinet/in.h> #include<string.h> #include<signal.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #include<poll.h> #include "read_write.h" #define ERR_EXIT(m) \ do { \ perror(m); \ exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while (0) int main(void) { int count = 0; signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); int listenfd; //被动套接字(文件描述符),即只可以accept, 监听套接字 if ((listenfd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP)) < 0) ERR_EXIT("socket error"); struct sockaddr_in servaddr; memset(&servaddr, 0, sizeof(servaddr)); servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr.sin_port = htons(5188); servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); int on = 1; if (setsockopt(listenfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &on, sizeof(on)) < 0) ERR_EXIT("setsockopt error"); if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)) < 0) ERR_EXIT("bind error"); if (listen(listenfd, SOMAXCONN) < 0) //listen应在socket和bind之后,而在accept之前 ERR_EXIT("listen error"); struct sockaddr_in peeraddr; //传出参数 socklen_t peerlen = sizeof(peeraddr); //传入传出参数,必须有初始值 int conn; // 已连接套接字(变为主动套接字,即可以主动connect) int i; struct pollfd client[2048]; int maxi = 0; //client[i]最大不空闲位置的下标 for (i = 0; i < 2048; i++) client[i].fd = -1; int nready; client[0].fd = listenfd; client[0].events = POLLIN; while (1) { /* poll检测[0, maxi + 1) */ nready = poll(client, maxi + 1, -1); if (nready == -1) { if (errno == EINTR) continue; ERR_EXIT("poll error"); } if (nready == 0) continue; if (client[0].revents & POLLIN) { conn = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&peeraddr, &peerlen); //accept不再阻塞 if (conn == -1) ERR_EXIT("accept error"); for (i = 1; i < 2048; i++) { if (client[i].fd < 0) { client[i].fd = conn; if (i > maxi) maxi = i; break; } } if (i == 2048) { fprintf(stderr, "too many clients\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("count = %d\n", ++count); printf("recv connect ip=%s port=%d\n", inet_ntoa(peeraddr.sin_addr), ntohs(peeraddr.sin_port)); client[i].events = POLLIN; if (--nready <= 0) continue; } for (i = 1; i <= maxi; i++) { conn = client[i].fd; if (conn == -1) continue; if (client[i].revents & POLLIN) { char recvbuf[1024] = {0}; int ret = readline(conn, recvbuf, 1024); if (ret == -1) ERR_EXIT("readline error"); else if (ret == 0) //客户端关闭 { printf("client close \n"); client[i].fd = -1; close(conn); } fputs(recvbuf, stdout); writen(conn, recvbuf, strlen(recvbuf)); if (--nready <= 0) break; } } } return 0; } |
小结:
(1)select函数受两点限制,而poll函数只受第一点(一个进程能打开的最大文件描述符个数)的限制。
(2)select和poll函数的共同点是:内核要遍历所有文件描述符,直到找到发生事件的文件描述符。——效率不容乐观。
